tax shield formula apv
Cash Flow After Deprecition And Tax 2 Depreciation Shield You. Tax rate debt load interest rate interest rate.
APV PVCF PVTS.

. Expected Tax Benefit from Borrowing The second step in this approach is the calculation of the expected tax benefit from a given level of debt. WACC Formula Cost of Equity of Equity Cost of Debt of Debt 1-Tax Rate read more and assume that this proposal is already considered in the calculation of the weighted average cost of capital WACC. Thereby the APV approach allows us to see whether adding more debt results in a tangible increase or decrease in value as well as enables us to quantify the effects of debt.
The Adjusted Present Value APV is a good calculation to use when appraising a potential investment. Using the tax shields from Table 17A2 the discounted value of these tax shields is calculated as. DE Current debtequity ratio.
The Present Value of Tax Shield pv ts is. However the APV is often considered to yield a more accurate valuation. The APV method is not used as frequently in practice as is the DCF analysis but more in academic circles.
Where CF - Cash Flow PC - Project Cost MR - Market Return RR - Risk Rate AB - Asset Beta IE - Interest Expense DR - Debt Rate TR - Tax Rate PVCF - PV of Cash Flows PVTS - Present Value of Tax Shield APV - Adjusted Present Value. As we know higher debt offers a higher tax shield which in turn increases both firm value and equity value. The discount rate used in the first part is the return on assets or return on equity if unlevered.
The intuition here is that the company has an 800000 reduction in taxable income since the interest expense is deductible. Pv cf cfr a mr - r100 - pc - 100 - 100 - 100 - - - pv cf Present Value of Tax Shield formula and calculations. Now that we have worked out all the intermediate calculations we can calculate adjusted present value as follows.
APV formula APV Unlevered NPV of Free Cash Flows and assumed Terminal Value NPV of Interest Tax Shield and assumed Terminal Value. Using the APV Method. NPV F 1 rn where PV Present Value F Future payment cash flow r Discount rate n the number of periods in the future.
The present value of the interest tax shield is therefore calculated as. _____ 1151 1135 1021 _____ 11352 1058. Tax Shield Formula Step By Calculation With Examples.
T o this end the tax shield itself is a derivativ e of the unlevered firm value. Based on the information do the calculation of the tax shield enjoyed by the company. Based on the previous method Marciniak derived the value of tax shield formula expressed in Eq.
The formula includes that comes from tax shield savings. We therefore assume that the firms WACC is 15 the borrowing rate is given above. The tax shield is defined as the value of the tax sa vings of interest paymen ts associated with the firm.
Interest Tax Shield Formula. Apv Adjusted Present Value Overview Components Steps. APV values the firm without leverage and then values the debt tax shields to determine the value of the whole firm.
Discount the FCF using the weighted average of after-tax debt costs and equity costs Adjusted Present Value APV. APV NPV L PV D 1061 million 10 million 2061 million Decision rule The decision rule for adjusted present value is the same as net present value. Present Value of Tax Shield Interest Expense Debt Rate Tax Rate Adjusted Present Value APV PV of Cash Flows Present Value of Tax Shield.
PV of Tax Shield 1050m0303170-0909 2. PV of Cash Flows Cash Flow Risk RateAsset Beta Market Return - Risk Rate - Project Cost. Pv ts e tcod pv ts pv ts pv ts pv ts.
This is equivalent to the 800000 interest expense multiplied by 35. APV base-case NPV sum of PVs of financing side effects. T Tax rate for the firm.
How to Calculate Adjusted Present Value APV To determine the. Its important to understand exactly how the NPV formula works in Excel and the math behind it. The present value of the interest tax shield for the period from 19891993 can be calcu-lated by discounting the annual tax savings at the pretax average cost of debt which was approximately 135 percent.
The interest tax shield can be calculated by multiplying the interest amount by the tax rate. Exercise 17 After Tax Cash Flows In Net Present Value Ysis Accounting For Management. PV TS i 1 N k C BT 1 k e i E28.
As such the shield is 8000000 x 10 x 35 280000. And stand for debt and equity of the firm and are the required return rates for debt and equity is the marginal tax rate. Debt And Taxes Chapter 15 In.
The following is the Sum of Tax-deductible Expenses Therefore the calculation of Tax Shield is as follows Tax Shield Formula 10000 18000 2000 40. When calculating for the present value of Tax shield and subsidy benefit on a loan does one has to add the issue cost of the loan to the amount of loan. This unlevered beta can then be used to arrive at the unlevered cost of equity.
In particular use of this approach effectively assumes that the company is not expected to grow which of course. To explicitly account for the debt tax shield the Adjusted Present Value APV method is used. This reduces the tax it needs to pay by 280000.
In we have a cash flow to the firm of and an absolute tax shield value of. Accept positive APV projects and reject negative APV projects. This model is similar to Harris and Pringle or Kaplan and Ruback model because the cost of equity is used as a discount factor assuming book value instead of market value.
It is the present value of an investment with some modifications. The Adjusted Present Value apv is. Value the project as if it were all-equity financed Add the PV of the tax shield of debt and other side effects D E E k D E D D WACC k 1 t E.
Issue cost 24m Amount of loan 50 m Normal borrowing rate 10 for 4 yrs Tax 30. Present Value of Cash Flows formula and calculations. The use of the MM formula 2 for the debt tax shield is a special case of the APV approach that makes somewhat restrictive assumptions about the level and risk of the debt tax shield.
We consider one time period starting at and ending at time. PV if Tax Shield 1050m24m0303170-0909. Adjusted Present Value Apv Definition Explanation Examples.
Plus the present value of debt financing costs. Interest Tax Shield Interest Expense x Tax Rate. The discount rate used in the second part is the cost of debt financing by period.

Capital Budgeting Considering Risk And Leverage Ppt Download

Adjusted Present Value Apv Formula And Excel Calculator

Adjusted Present Value Apv Formula And Excel Calculator

Materi Ke 5 Financial Management Bagian Ii Kelas Ap 1 Ppt Download

Capital Budgeting And Valuation With Leverage Ppt Video Online Download

Resolution Of Tax Shield On Interest Expense In Wacc Edward Bodmer Project And Corporate Finance
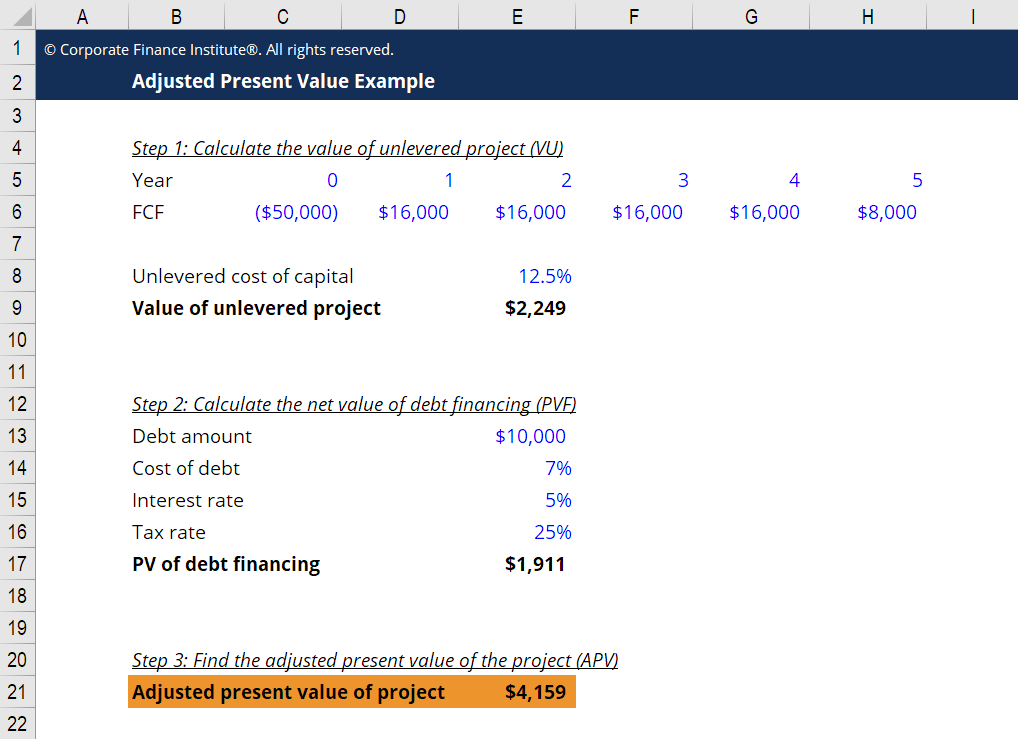
Adjusted Present Value Apv Definition Explanation Examples

Ppt Corporate Finance Financing And Valuation Powerpoint Presentation Id 540390
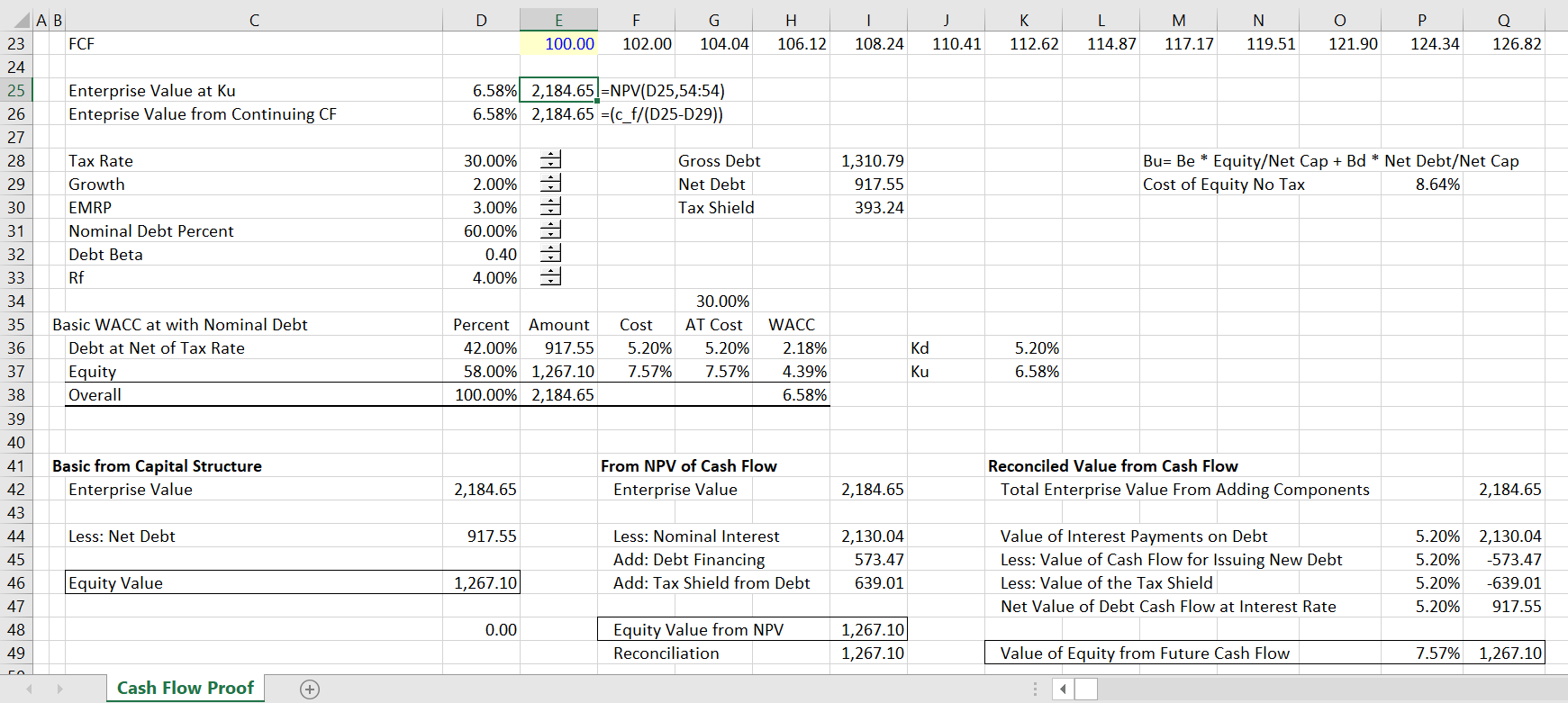
Resolution Of Tax Shield On Interest Expense In Wacc Edward Bodmer Project And Corporate Finance

Lecture 09 Valuation Berk De Marzo Chapter 18 Pdf Free Download

Using Apv A Better Tool For Valuing Operations Cost Accounting Finance Operator
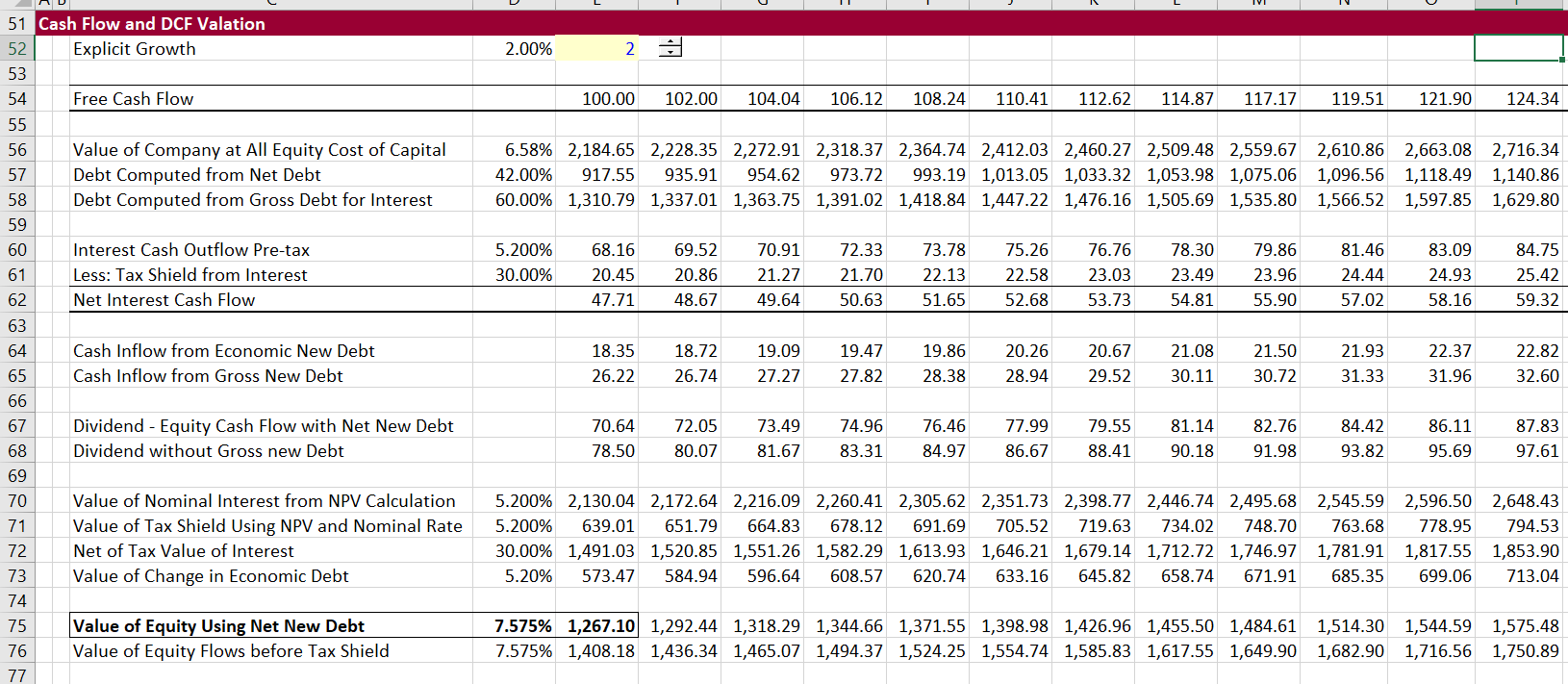
Resolution Of Tax Shield On Interest Expense In Wacc Edward Bodmer Project And Corporate Finance

Adjusted Present Value Apv Formula And Excel Calculator

Wacc Diagram Explaining What It Is Cost Of Capital Financial Management Charts And Graphs

Adjusted Present Value Apv Formula And Excel Calculator

Apv Adjusted Present Value Overview Components Steps

Capital Budgeting And Valuation With Leverage Ppt Video Online Download

Ppt Chapter 21 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 4710282
